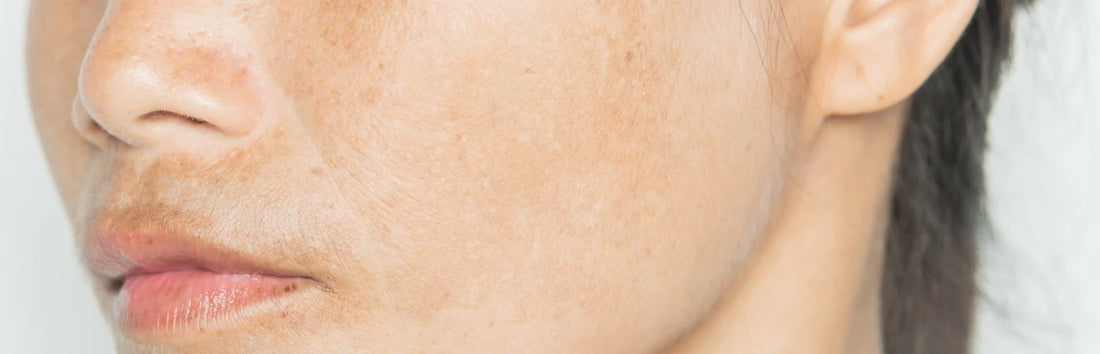
Have you been struggling with dark patches and uneven skin tone that never seem to get better? If you’re tired of wasting your time, money and energy on endless products, experimenting with active ingredients and yet not getting any results then this blog is here for you.
Countless people struggle with hyperpigmentation. In this blog, we'll talk about hyperpigmentation, uncover its causes, symptoms, and effective treatment options.
Get ready to say goodbye to those dark spots and hello to a bright and more even skin tone!
What is hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation, simply put, is a skin condition in which certain parts of skin become darker than the surrounding area.
It happens when the skin produces an excess of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin colour. We will talk about this more in the blog later.
Hyperpigmentation can appear as dark spots , big patches, small dots, or may even be larger symmetrical spots. These can appear on the face or other areas of the body but hyperpigmentation generally occurs more on sun exposed areas.
Now let's talk about signs and symptoms of hyperpigmentation in brief!
Understanding how hyperpigmentation happens?
When the skin goes through a painful experience of injury, inflammation, or excessive sun exposure, it tries to protect itself by producing melanin.
In these situations when melanin is over produced by the skin it leads to the formation of hyperpigmented areas.
What is melanin?
Melanin is a pigment produced by specialised cells called melanocytes.
Its job is to protect the skin.It acts as a natural sunscreen, absorbing harmful UV rays from the sun and preventing damage to skin cells.
It also provides pigment that determines the colour of our skin, hair and eyes.
Signs of Hyperpigmentation
As explained earlier hyperpigmentation is characterised by dark spots and patches. To be more precise hyperpigmentation signs appear as:
- Darkened patches of skin: These spots or patches can vary in size, shape, and colour, ranging from brown, black, grey, red, or pink.
- Uneven skin tone: The affected areas are noticeably darker than the surrounding skin.
- No pain or itchiness: Hyperpigmentation is typically not accompanied by any form of discomfort.
Now that we know what hyperpigmentation looks like, let’s talk about different types of Hyperpigmentation and discuss their causes in brief.
Types of Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation is an umbrella term for different types of dark spots, patches and skin damage that exist for a long period of time.
Different types of hyperpigmentation tend to have different causes and treatments also differ for all of them, so let’s start going through major types of hyperpigmentation:
- Melasma
This type of hyperpigmentation appears as brown or greyish-brown patches which are often symmetrical.
They primarily occur on face and are caused by hormonal changes (pregnancy, birth control), sun exposure & genetics.
More common in women and can worsen during pregnancy or while taking hormonal contraceptives.
- Sunspots (Solar Lentigines)
Sunspots are small, flat, brown spots. spots caused by excessive sun exposure over time.
Typically these occur on sun-exposed areas like the face, hands, and shoulders.This is more common in fair-skinned individuals and can increase with age.
- Post-inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
PIH are flat, brown spots or patches that result from inflammation like acne, eczema, injuries, or other skin inflammation.
These often fade over time but can be persistent in some cases.
- Age Spots (Lentigines)
Age spots are again brown spots but these are associated with ageing or sun damage over a long period and are commonly found on sun-exposed areas like the face, hands, and arms.
This is more prevalent in older individuals and often increases in number with age.
- Freckles (Ep freckles)
These are a group of very tiny dot like flat brown spots often present from childhood caused by genetics and sun exposure.
Now that we know what all types of hyperpigmentation look like, let’s also be aware of types of skin discolouration that don't come under hyperpigmentation.
What is Not Hyperpigmentation?
Certain skin conditions might be mistaken as hyperpigmentation but are not like:
Conditions Involving Less Melanin
- Hypopigmentation: This is the opposite of hyperpigmentation, where patches of skin become lighter.
- Vitiligo: A condition where patches of skin lose their colour entirely.
- Albinism: A genetic condition where little or no melanin is produced.
Other Skin Conditions
- Eczema: While it can cause skin discoloration, it's primarily an inflammatory condition.
- Psoriasis: Similar to eczema, it causes skin inflammation and can lead to discoloration.
- Rosacea: This condition causes redness and flushing of the skin.
- Acne: While it can lead to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, acne itself is not hyperpigmentation
Also, temporary skin discoloration like sunburns and bruises can cause temporary darkening of skin , but are not hyperpigmentation specifically.
Causes of Hyperpigmentation
We already know that over production of melanin is responsible for hyperpigmentation, but let’s dive deeper into what factors cause this overproduction of melanin or hyper pigmentation so you are better equipped to prevent and treat hyperpigmentation.
- Sun Exposure: Excessive sun exposure is the most common cause of hyperpigmentation. UV rays cause melanin production, leading to darker patches.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menopause or for people suffering from PCOS can lead to different types of hyperpigmentation
- Medications: Certain medications can induce hyperpigmentation as a side effect too like birth control pills and some antibiotics etc
- Genetics: A family history of hyperpigmentation can increase one’s risk.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: While less common, deficiencies in certain vitamins and minerals can contribute to skin discoloration.
- Skin Inflammation:
- Acne: Inflammatory acne can lead to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH).
- Eczema: Chronic inflammation which comes with eczema can cause darkened areas.
- Psoriasis: Similar to eczema, inflammation in psoriasis also can lead to hyperpigmentation.
- Other skin injuries like Burns, cuts, or scrapes can trigger PIH.
It's important to note that there might be other medical, rare or specific causes that aren't mentioned here.If you're concerned about hyperpigmentation, consulting a dermatologist is always recommended for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
How to prevent Hyperpigmentation?
Now that you know all the factors that cause hyperpigmentation, you can protect your skin with proper care. Here are some key steps:
- Wear sunscreen daily: Opt for a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher. Pro tip: If you have hyperpigmentation, choose a mineral-based sunscreen, especially a tinted one. Mineral sunscreens reflect UV rays, protecting your skin like a shield, while chemical sunscreens absorb UV and generate heat, which can worsen dark spots. Tinted options also defend against visible light, offering extra protection for hyperpigmented skin.
- Seek shade: Limit sun exposure, especially during peak hours (10 AM to 2 PM).
- Protective clothing: Wear hats, sunglasses, and long-sleeved clothing when outdoors.
- Gentle cleansing: Use a mild cleanser to avoid irritating the skin.
- Follow a Consistent skincare routine - Regular cleansing, exfoliation, and moisturising help remove dead skin cells, prevent clogged pores, and maintain skin health, reducing the risk of dark spots and uneven skin tone.
- Avoid harsh products: Steer clear of products containing alcohol, fragrances, or other irritating ingredients.
- Avoid skin picking: Picking at blemishes can lead to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
- Balanced diet: A diet rich in antioxidants can support overall skin health.
- Regular check-ups: Consult a dermatologist for professional advice and treatment options.
How harmful is hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation, even though usually harmless, can be a cosmetic concern for many people and can impact one‘s confidence leading to severe emotional impact
- It can make individuals feel self-conscious about their appearance, leading to a constant awareness of their skin and can contribute to feelings of low self-esteem.
- The fear of judgment or negative reactions from others also tends to cause anxiety in social situations.
- Due to self-consciousness and anxiety, individuals might withdraw from social interactions to avoid scrutiny.
- The emotional burden of hyperpigmentation can lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness.
- The constant effort to cover up or hide the hyperpigmentation can be emotionally draining and exhausting.
And that’s why it becomes important for people to treat hyperpigmentation.
Treating Hyperpigmentation: A Comprehensive Guide.
As already mentioned, different types of hyperpigmentation are caused by different reasons, and thus the treatment also differs for each type of hyperpigmentation .
So before you get started with any treatment routine, go back and figure out the reason and type of your hyperpigmentation.
At-Home Care
Starting with at home care that is best for mild hyperpigmentation caused by sun exposure or inflammation.
You need to:
- Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher daily, even on cloudy days.
- Gently exfoliate regularly to remove dead skin cells, revealing a brighter complexion. Look for products containing salicylic acid.
- Maintain a healthy diet rich in food that contains vitamin C and antioxidants.
- Hydrate your skin and your body well
- Avoid harsh ingredients in skin care.
- Make sure that everything that comes in touch with your skin right from the fabric of your pillow covers to the skin product you use is harmless, gentle, and clean.
- Follow a consistent skincare routine, consisting of gentle cleansing, toning, moisturising, and if needed over-the-counter treatment for hyperpigmentation targeted skincare which we will be discussing next.
Hyperpigmentation targeted skincare
A lot many types of hyperpigmentation can be resolved with targeted skincare treatment. One can opt for over-the-counter topical creams, skin care products, marketed for hyperpigmentation or even DIY skincare routines.
Let’s discuss each of these thoroughly.
Over the counter, topical creams & serums
Skincare products or OC creams that are generally marketed for hyperpigmentation have one of the ingredients:
- Microalgae
- Azelaic acid
- Kojic acid
- Niacinamide
- AHAs & BHAs, etc
These ingredients help with exfoliation, melanin reduction, and improvement in skin texture.
But all of these ingredients have different properties and what may suit one individual might not work for another.
That is why it’s important that you take into consideration all the different factors that matter like your skin type, your skin concerns how sensitive your skin is and the pros & cons of each ingredient.
To help you out here is a brief on all the things you need to know on specific ingredients before you get started with products to get rid of hyperpigmentation:
Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs)
- How it works: AHAs like glycolic, lactic, and citric acids dissolve the bonds between dead skin cells, promoting exfoliation. This helps to reveal a brighter, more even skin tone.
- Pros: Exfoliates dead skin cells, improves skin texture, and can stimulate collagen production.
- Skin types: Suitable for most skin types, but those with sensitive skin should start with lower concentrations.
- Cons: AHAs can increase sun sensitivity, so always use sunscreen, can be used once in a while only as it’s a strong potent ingredient.
Beta Hydroxy Acid (BHA)
- How it works: Salicylic acid, the primary BHA, penetrates oil-based substances and exfoliates dead skin cells within pores.
- Pros: Exfoliates, helps to unclog pores, and reduces inflammation.
- Skin types: Ideal for oily and acne-prone skin due to its oil-soluble properties.
- Cons: Can be drying, so it's essential to moisturise regularly and like AHA this also shall not be used everyday.
Retinol
- How it works: Increases cell turnover, stimulates collagen production, and helps to regulate melanin production.
- Pros: Improves skin texture, reduces fine lines, and can lighten dark spots.
- Skin types: Suitable for most skin types, but those with sensitive skin should start with a lower concentration.
- Cons: Can cause irritation, dryness, and increased sun sensitivity. Shall be added to routine after careful consideration,
Vitamin C
- How it works: Antioxidant that inhibits melanin production, protects against free radicals, and boosts collagen synthesis.
- Pros: Brightens skin, improves skin tone, and protects against environmental damage.
- Skin types: Suitable for most skin types.
- Cons: Can be unstable, so look for formulations with antioxidants to protect the vitamin C.
Niacinamide
- How it works: Reduces inflammation, improves skin barrier function, and inhibits melanin transfer.
- Pros: Even skin tone, improves texture, and helps to strengthen the skin's protective barrier.
- Skin types: Suitable for all skin types, including sensitive skin.
- Cons: Generally well-tolerated, but some people may experience temporary redness or flushing.
Azelaic Acid
- How it works: Has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, inhibits tyrosinase, and exfoliates dead skin cells.
- Pros: Effective for both acne and hyperpigmentation, reduces redness, and improves skin texture.
- Skin types: Suitable for most skin types, including sensitive skin.
- Cons: Can cause mild irritation initially.
Kojic Acid
- How it works: Inhibits tyrosinase, reducing melanin production.
- Pros: Brightens skin and helps to fade dark spots.
- Skin types: Suitable for most skin types, but those with sensitive skin should use it cautiously.
- Cons: Can cause skin irritation in some individuals.
Tranexamic Acid
- How it works: Inhibits the formation of melanin, reduces inflammation, and improves blood vessel function.
- Pros: Brightens skin, reduces redness, and improves overall skin tone.
- Skin types: Suitable for most skin types.
- Cons: Relatively new ingredient, with limited long term studies.
Microalgae Extract
- How it works: unlike any of the other products, microalgae doesn’t just lighten the overall skin tone and colour, it specifically identifies and targets those spots. It works on controlling, reducing and preventing overproduction of melanin (in the future too!)
- Benefits: Boosts collagen, reduces dark spots, is rich in antioxidants, anti-inflammatory, sun protection,evens skin tone, suitable for long term use.
- Skin types: Suitable for most skin types.
- Cons: Relatively new ingredient in Indian market with limited availability.
Read more on ‘Microalgae in Skincare’ in the blog section
Ingredients for DIY skincare for hyperpigmentation
Licorice Extract
- How it works: Contains glabridin, which inhibits tyrosinase and has anti-inflammatory properties.
- Benefits: Brightens skin, reduces inflammation, and soothes irritation.
- Skin types: Suitable for most skin types.
- Caution: Generally well tolerated, but individual sensitivities may occur.
Aloe Vera
- How it works: Contains soothing and hydrating properties, with potential antioxidant benefits.
- Benefits: Calms irritated skin, provides hydration, and may have mild brightening effects.
- Skin types: Suitable for all skin types, especially sensitive and irritated skin.
- Caution: Not a primary treatment for hyperpigmentation, but can complement other ingredients.
Note: for hyperpigmentation, effects may be limited.
Papaya
- How it works: Contains papain, an enzyme that helps exfoliate dead skin cells and brighten the complexion.
- Best for: Mild hyperpigmentation, especially post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
- Application: Mash ripe papaya to create a pulp, apply it to the skin, leave for 15-20 minutes, then rinse off.
Honey
- How it works: Has antibacterial and antioxidant properties that can soothe the skin and promote healing.
- Best for: Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
- Application: Apply raw honey directly to the affected area, leave for 15-20 minutes, then rinse off.
Cucumber
- How it works: Has cooling and hydrating properties that can soothe irritated skin and reduce inflammation.
- Best for: Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
- Application: Grate a cucumber to extract its juice, apply it to the skin, leave for 15-20 minutes, then rinse off.
Sandalwood
- How it works: Has anti-inflammatory and skin-soothing properties.
- Best for: Mild hyperpigmentation, especially melasma.
- Application: Mix sandalwood powder with water or rose water to form a paste, apply it to the skin, leave for 15-20 minutes, then rinse off.
Clinical Treatments
For severe hyperpigmentation , general skincare and over the counter treatment might not work or give inconsistent results.
In that case one shall consult a dermatologist. There are a wide range of treatments available at derma offices that can help get rid of hyperpigmentation.
- Chemical Peels: In chemical peels acids are used to remove the outer layers of skin, revealing smoother & even-toned skin.
- Microdermabrasion: It involves using a device to exfoliate the skin's surface.
- Laser Therapy: Different types of lasers are used to target and reduce hyperpigmentation.
- Prescription Medications: For severe cases, dermatologists might prescribe stronger topical treatments or oral medications.
Things to take note of: Hyperpigmentations can not be treated overnight. One needs to:
- Be Consistent: Most treatments require consistent use to see results. Be patient and follow your dermatologist's recommendations.
- Patch test: It’s important to do a patch test for new products before you apply them to your entire face.
- Protect Skin: Even after treatment, continue to protect your skin from the sun to prevent hyperpigmentation from returning.
- Hydrate: Make sure you are drinking plenty of water and using a moisturiser.
- Avoid Irritants: Harsh soaps, scrubbing, and excessive heat can worsen hyperpigmentation.
- Consult a Dermatologist: For persistent or severe hyperpigmentation, seeking professional guidance is essential.
Remember, the best treatment approach depends on the type and severity of your hyperpigmentation, as well as your skin type and overall health.